The digestive process first occurs in the oral cavity. Oral cavity is
limited by several parts, namely the over the bones of the jaw and
palate (palate), the left and right by the muscles of the cheek, and the
bottom of the lower jaw.
Oral cavity (cavum Oris)
Oral cavity is the beginning of the digestive tract of food. In the oral cavity, furnished means of digestion and digestive glands to help digestion of food.
a. Dental (dentis)
Has the function of cut, tear and grind food into small particles. Teeth are embedded in the jaw and strengthened by the gum.
Parts of the tooth is as follows:
- Dental Crown
This section is coated by email and in dlamnya contained dentin (bone tooth). Email layer contains a substance which is very hard, yellowish-white, and glossy. Email contains a lot of calcium salt.
- Dental Bones
Dental bone located under the layer of email. Dental bone includes two parts, the neck of the tooth and tooth root. Sections of bone surrounded teeth gums tooth called the neck, while the dental bones that are embedded in the jaw bone is called the root of the tooth. The roots of teeth attached to the wall of the jaw bone with cement intermediaries.
- Dental Cavities
Tooth cavity located inside the tooth. Inside the tooth cavity contained blood vessels, connective tissue, and tissue saraf.oleh therefore, tooth cavity is very sensitive to heat and cold stimuli.
According to its shape, the teeth can be divided into four types, namely:
- Incisor (incisors / I), serves to cut up food.
- Dental fang (canine / C), serves to tear up food.
- Molar front (Premolare / P), serves to soften the food.
- Rear molar (Molare / M), serves to soften the food.
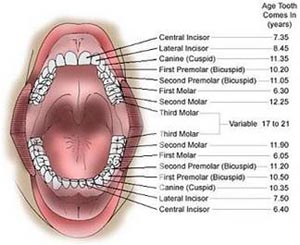
In humans, there are two generations of so-called nature diphydont teeth. Generation teeth are milk teeth and teeth are milk teeth permanent. tooth owned by children aged 1-6 years. The amount is 20 pieces. While the permanent teeth are owned by the children over 6 years, the numbers 32 pieces.
b. Tongue (lingua)
The tongue forms the floor of the oral cavity. The back of the tongue muscles attached to the hyoid bone.
Tongue tersiri of 2 types of muscle, namely:
- Extrinsic muscles of the tongue berorigo outside, insertion of the tongue.
- Intrinsic muscles of berorigo and insertion within the tongue.
Working the muscles of the tongue can be moved above 3 parts, namely: root lingua (tongue base), the dorsum of the lingua (tongue back), the apex lingua (tongue tip).
The tongue serves to help chew food that is in terms of turning the food in the mouth, aids in swallowing food, as the sense of taste, and help in speaking.
As the sense of taste, on the surface of the tongue are taste nerve cell bodies (papillae).
There are three types of papillae, namely:
- Papilla fungiformis, shaped like a mushroom, located on the side of the tongue and the tip of the tongue.
- Papilla filiformis, shaped fine threads, is located at 2 / 3 the front of the tongue.
- Papilla serkumvalata, round, situated compile like inverted V at the back of the tongue.
The tongue has 10,000 taste nerves, but can only detect four taste sensations: sweet, sour, bitter, and salty.
c. Salivary gland
Foods are digested with the aid of mechanical teeth, are chemically with the help of enzymes produced by salivary glands. Salivary glands produce saliva contains. Saliva contains amylase enzymes that function ptyalin atu convert starch into sugars or starch or maltose.
Salivary gland consists of three pairs as follows:
- Parotid gland, located below the ear. These glands produce saliva, a liquid called the serosa. Paotis gland is the largest gland in the cheek side empties in dealing with the second molars.
- Glands submandibularis / submaksilaris, located below the lower jaw.
- Sublingualis gland, located under the tongue.
Sublingualis submandibularis gland and produces water and the lender called Iseromucus. The two glands that empty into the edge of the tongue.
Oral cavity (cavum Oris)
Oral cavity is the beginning of the digestive tract of food. In the oral cavity, furnished means of digestion and digestive glands to help digestion of food.
a. Dental (dentis)
Has the function of cut, tear and grind food into small particles. Teeth are embedded in the jaw and strengthened by the gum.
Parts of the tooth is as follows:
- Dental Crown
This section is coated by email and in dlamnya contained dentin (bone tooth). Email layer contains a substance which is very hard, yellowish-white, and glossy. Email contains a lot of calcium salt.
- Dental Bones
Dental bone located under the layer of email. Dental bone includes two parts, the neck of the tooth and tooth root. Sections of bone surrounded teeth gums tooth called the neck, while the dental bones that are embedded in the jaw bone is called the root of the tooth. The roots of teeth attached to the wall of the jaw bone with cement intermediaries.
- Dental Cavities
Tooth cavity located inside the tooth. Inside the tooth cavity contained blood vessels, connective tissue, and tissue saraf.oleh therefore, tooth cavity is very sensitive to heat and cold stimuli.
According to its shape, the teeth can be divided into four types, namely:
- Incisor (incisors / I), serves to cut up food.
- Dental fang (canine / C), serves to tear up food.
- Molar front (Premolare / P), serves to soften the food.
- Rear molar (Molare / M), serves to soften the food.
In humans, there are two generations of so-called nature diphydont teeth. Generation teeth are milk teeth and teeth are milk teeth permanent. tooth owned by children aged 1-6 years. The amount is 20 pieces. While the permanent teeth are owned by the children over 6 years, the numbers 32 pieces.
b. Tongue (lingua)
The tongue forms the floor of the oral cavity. The back of the tongue muscles attached to the hyoid bone.
Tongue tersiri of 2 types of muscle, namely:
- Extrinsic muscles of the tongue berorigo outside, insertion of the tongue.
- Intrinsic muscles of berorigo and insertion within the tongue.
Working the muscles of the tongue can be moved above 3 parts, namely: root lingua (tongue base), the dorsum of the lingua (tongue back), the apex lingua (tongue tip).
The tongue serves to help chew food that is in terms of turning the food in the mouth, aids in swallowing food, as the sense of taste, and help in speaking.
As the sense of taste, on the surface of the tongue are taste nerve cell bodies (papillae).
There are three types of papillae, namely:
- Papilla fungiformis, shaped like a mushroom, located on the side of the tongue and the tip of the tongue.
- Papilla filiformis, shaped fine threads, is located at 2 / 3 the front of the tongue.
- Papilla serkumvalata, round, situated compile like inverted V at the back of the tongue.
The tongue has 10,000 taste nerves, but can only detect four taste sensations: sweet, sour, bitter, and salty.
c. Salivary gland
Foods are digested with the aid of mechanical teeth, are chemically with the help of enzymes produced by salivary glands. Salivary glands produce saliva contains. Saliva contains amylase enzymes that function ptyalin atu convert starch into sugars or starch or maltose.
Salivary gland consists of three pairs as follows:
- Parotid gland, located below the ear. These glands produce saliva, a liquid called the serosa. Paotis gland is the largest gland in the cheek side empties in dealing with the second molars.
- Glands submandibularis / submaksilaris, located below the lower jaw.
- Sublingualis gland, located under the tongue.
Sublingualis submandibularis gland and produces water and the lender called Iseromucus. The two glands that empty into the edge of the tongue.
No comments:
Post a Comment